Programmable Auxetic Mid-sole
Research | MIT Design Lab | 2017 | In collaboration with Yihyun Lim, Hunmin Koh, Will Walker
*Due to the NDA agreement with the sponsor of this research project, the documentation in this page is partial and non-detailed.
“Programmable Auxetics” is an exploration into Auxetic Metamaterials to create a programmable material with tunable stiffness for application in high-performance running shoe midsoles. We have created a platform for design, simulation and fabrication of 2D Auxetic-based metamaterials to be used in injection moldable midsoles. The goal is to create a high-performance running shoe midsole with spatially-tunable mechanical properties, which is programmed according to the performance requirements including load cycles, impact energy dissipation, and deflection.
The conventional method in creating running shoe soles relies on the properties of base material. In order to satisfy performance requirements such as impact damping, cushioning, and lateral support, separate layers of different materials are joined and adhered together. This forces a high limitation toward achieving customization and tunable properties. Through the approach established in this project, instead of relying on properties of the base material itself, the overall material behavior can be programmed through variations in the cellular macro and meso structure. We’ve established a workflow combining Computational Design and Finite Element Modeling(FEM) a to design and optimize mesostructured midsoles based on force-mapped running data and functional requirements. In the manufacturing stage, the product of design process can be manufactured with mass-manufacturing method of injection molding.
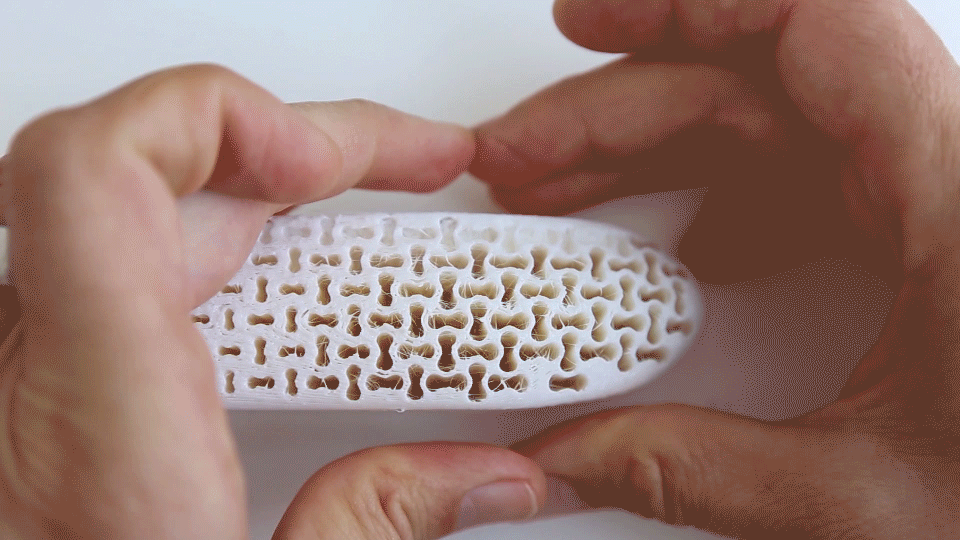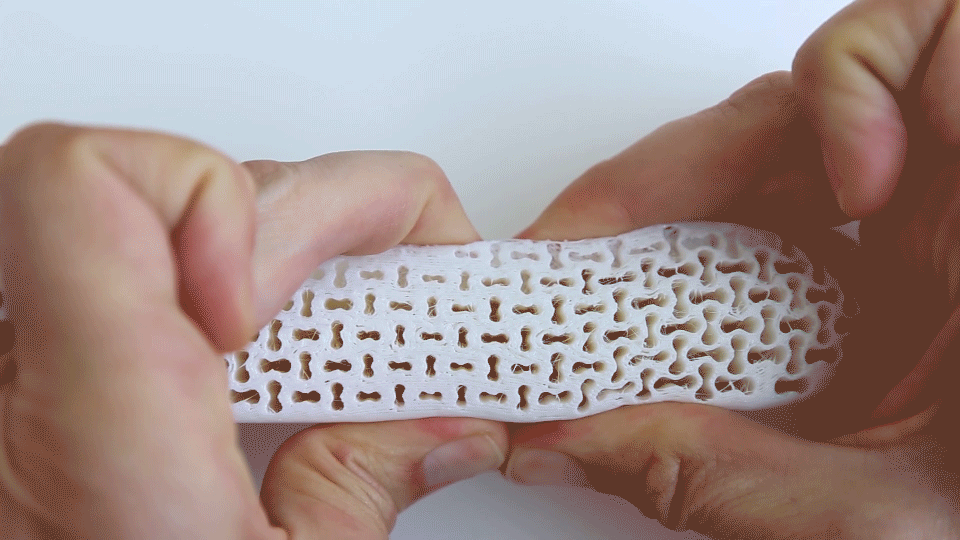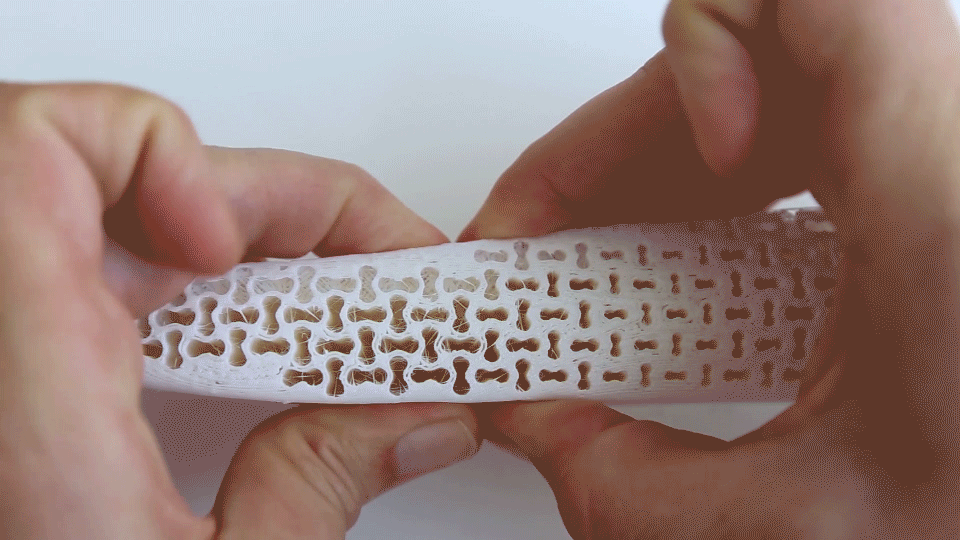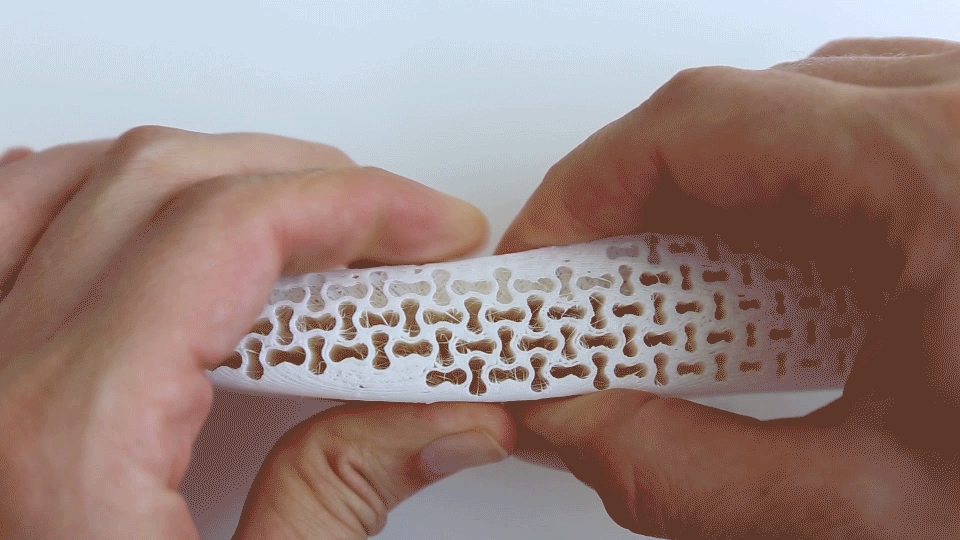 Exploring midsole behavior under force, representing variable cushioning in functional zones for maximum comfort. |  Simulation and physical testing of Re-curve pattern, exhibiting its dual deformation phases corresponding to walking (high-cushioning/ maximum comfort) and running (higher stiffness for bottoming-up prevention) activities. |
|---|---|
 FEM Simulation of Auxetic Re-curve pattern representing its dual-deformation phases. |  exploration into different Auxetic structural patterns. |
 Evaluation of different design parameters through FEM simulation |